Closed-source large language models have undergone several iterations over the past few months, but they have also experienced information leakage issues—a real concern. However, you might more want to find whether you can run LLMs and perform tasks locally. While you can run ChatGPT-quality AI on your own computer—privately, using the GPU you might already have.
This guide cuts through the technical jargon to provide a clear, straightforward path. You will learn how to evaluate your current graphics card (GPU), understand what kind of AI models it can handle, and ultimately choose the right setup to get the best performance for your budget. Our goal is to make running a private AI simple, putting you back in control of your data.
CONTENT:
Understanding GPU Requirements for Local LLMs
Before discussing specific GPU recommendations, it's crucial to understand the fundamental concepts that determine whether a GPU can effectively run a language model. These concepts will guide every hardware decision you make.
VRAM (Video RAM)
VRAM is the GPU's dedicated memory—the workspace where the model resides during inference. For language models, VRAM is the foundation of LLM performance: the model must fit in VRAM or it won't load, and relying on system RAM will severely degrade performance.
Rule of thumb: roughly 2 GB of VRAM per billion parameters at FP16.
- A 7B model needs ~14 GB
- A 13B model needs ~26 GB
Quantization (below) can reduce these requirements substantially.
Don't have a high-end GPU?
Run optimized models (under 5B) instantly. Nut Studio simplify the setup so you can pick and deploy LLMs without the expensive hardware upgrades or deep tech skills.
Memory Bandwidth
Memory bandwidth (GB/s) is how quickly a GPU can move data within VRAM. It directly affects token generation speed—how responsive the model feels. A GPU with ample VRAM but low bandwidth may still load models, but it will respond slowly.
However, older GPUs with generous VRAM can still perform well, as they keep both the full model and KV cache on-GPU—avoiding CPU offload that would negate bandwidth or architectural advantages.
Modern GPUs like the RTX 4090 exceed 1000 GB/s; older or budget cards may offer 400–600 GB/s. For interactive use, aim for ≥600 GB/s to keep conversations fluid.
Quantization
Quantization reduces weight precision (e.g., FP16 → INT8/INT4), shrinking the VRAM footprint and allowing models 2–4× larger to run on the same hardware—often with minimal or even imperceptible quality loss for typical use.
Example: a 13B model that needs ~26 GB at FP16 can often run in 8–10 GB when quantized to 4-bit. Fitting bigger models into smaller VRAM.
VRAM Requirements by Model Size
Don't worry about manual configuration. Our tool auto-detects your GPU and sets up the best model for you in one click.
| Model Size | FP16 (Full Precision) | INT8 (8-bit Quantized) | INT4 (4-bit Quantized) | Minimum GPU | Action Now |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7B | 14GB | 7GB | 3.5GB | RTX 3060 12GB | Download |
| 7B | 14GB | 7GB | 3.5GB | RTX 3060 12GB | Download |
| 13B | 26GB | 13GB | 6.5GB | RTX 3080 10GB (INT4) | Download |
| 30B | 60GB | 30GB | 15GB | RTX 4090 24GB (INT4) | Download |
| 70B | 140GB | 70GB | 35GB | RTX 6000 Ada 48 GB(single GPU), 2× RTX 3090 with NVLink (INT4) |
Download |
Our Top GPU Picks for Local LLMs in 2026
Now that you understand the key metrics, here are our specific GPU recommendations for every budget and use case. NVIDIA's CUDA platform is the industry standard, making these cards the path of least resistance for local AI.
1 Best Consumer Picks: NVIDIA GPUs
NVIDIA's CUDA platform has become the industry standard for AI workloads, offering unmatched software support and optimization. Every major LLM framework—from PyTorch to TensorFlow—is built with CUDA in mind, making NVIDIA GPUs the path of least resistance for local deployment.
NVIDIA RTX 4090
- Pros: Still a powerhouse with 24GB of VRAM, now serving as the high-end alternative to the 5090. It offers excellent performance for most local LLMs and provides a better value proposition than the 5090 for users who don't strictly need the extra 8GB of memory. You can comfortably run quantized 30B models or experiment with 70B models.
- Cons: Remains expensive, though prices may have softened slightly with the 50-series launch. Its 24GB buffer is now the second-largest in the consumer class, which acts as a hard limit for the very largest models.
NVIDIA RTX 5090
- Pros: The new undisputed king of consumer AI with 32GB of GDDR7 VRAM. It features a massive memory bandwidth of nearly 1.8 TB/s (almost double that of the 4090), significantly accelerating token generation speeds. This card allows you to run unquantized 30B models comfortably or larger 70B–100B parameter models with decent context windows entirely in memory.
- Cons: Although the performance is improved by 20-30%, the cost has also increased by more than 30%, making it less cost-effective than the 4090.
Quick Compare: RTX 4090 vs RTX 5090
| Spec | RTX 4090 | RTX 5090 | Improvement | Impact on AI / LLMs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Ada Lovelace | Blackwell (5nm) | Next Gen | Supports FP4 precision; doubles AI performance. |
| VRAM | 24GB GDDR6X | 32GB GDDR7 | +33% | Run 30B+ parameter models natively without heavy quantization. |
| Bandwidth | 1,008 GB/s | 1,792 GB/s | +78% | Significantly reduces inference latency for large models. |
| CUDA Cores | 16,384 | 21,760 | +33% | Major boost in raw computational power. |
| AI Compute (FP4) | Not Supported | 3,352 TOPS | New Feature | Increases large model inference speed by over 45%. |
| TGP (Power) | 450W | 575W | +28% | Requires a high-wattage, robust power supply unit (PSU). |
The RTX 4090 is still far from obsolete, but the RTX 5090 represents a clear performance upgrade. If you already own an RTX 4090 and don't require the absolute maximum performance for your use case, it remains an excellent choice. However, if your work frequently involves running large models (30B+ parameters) and demands high-speed responsiveness, then upgrading to the RTX 5090 is a worthwhile consideration.
2 Professional and High-End Uses
NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada Generation
- Pros: A massive 48GB of VRAM, essential for training, fine-tuning, and running very large models without compromise. Supports advanced enterprise workflows.
- Cons: Very high cost, designed for workstations, not typical desktops.
NVIDIA A100
- Pros: Proven reliability for enterprise and cloud environments. Available with up to 80GB of VRAM for handling enormous models and datasets.
- Cons: Extremely expensive and designed for data centers, not local desktop use. Overkill for 99% of users.
3 Budget-Conscious GPU Picks
Not everyone can accept flagship GPU prices, and thankfully, with the fast updates of GPUs, the used market offers exceptional opportunities for budget-conscious LLM enthusiasts. For language model work, the key is that older GPUs with large VRAM pools often outperform newer GPU models with less memory.
NVIDIA RTX 3090 24GB
- Pros: Best budget option. Available for $700-900 used, it matches the RTX 4090's VRAM capacity while delivering 70-80% of its performance. This is the undisputed value champion, capable of running 30B models comfortably and even stretching to 70B with aggressive quantization.
- Cons: Used market availability can be inconsistent, and you're buying older hardware without warranty coverage in most cases.
RTX 4070 Ti Super 16 GB
- Pros: A practical sweet spot for 7B–13B models with longer contexts, offering excellent perf-per-watt without the heat and noise tax of older high-end cards.
- Cons: Costs more than older cards and still not enough VRAM for easy 30B.
RTX 4090 vs 4080 vs 4070 Ti: Local LLM Reality Check
RTX 4090 (24GB VRAM)
Represents the easiest path to larger models and longer context windows with minimal workarounds. You can load 30B models at 8-bit quantization while maintaining 8K+ token contexts, or push to 70B models with 4-bit quantization. The extra 8GB over the 4080 eliminates constant VRAM anxiety and allows for comfortable experimentation. Token generation typically reaches 40-50 tokens/second on 13B models.
RTX 4080 (16GB VRAM)
Delivers strong throughput and handles 13B-33B quantized models comfortably. However, you'll need to watch context length and batch size carefully. Extended conversations or document analysis can push VRAM limits. Expect 30-35 tokens/second on 13B models—still excellent for interactive use but requiring more careful resource management.
RTX 4070 Ti (12GB VRAM)
Offers efficiency and competence for 7B and quantized 13B models, but you'll hit VRAM walls sooner than you'd like. Long context windows become problematic, and forget about experimenting with larger models without aggressive quantization. Token generation hovers around 25-30 tokens/second on 7B models—acceptable but limiting for advanced use cases.
Price-to-Performance Analysis
When evaluating GPUs for local LLM deployment, start with a simple calculation: VRAM capacity divided by price.
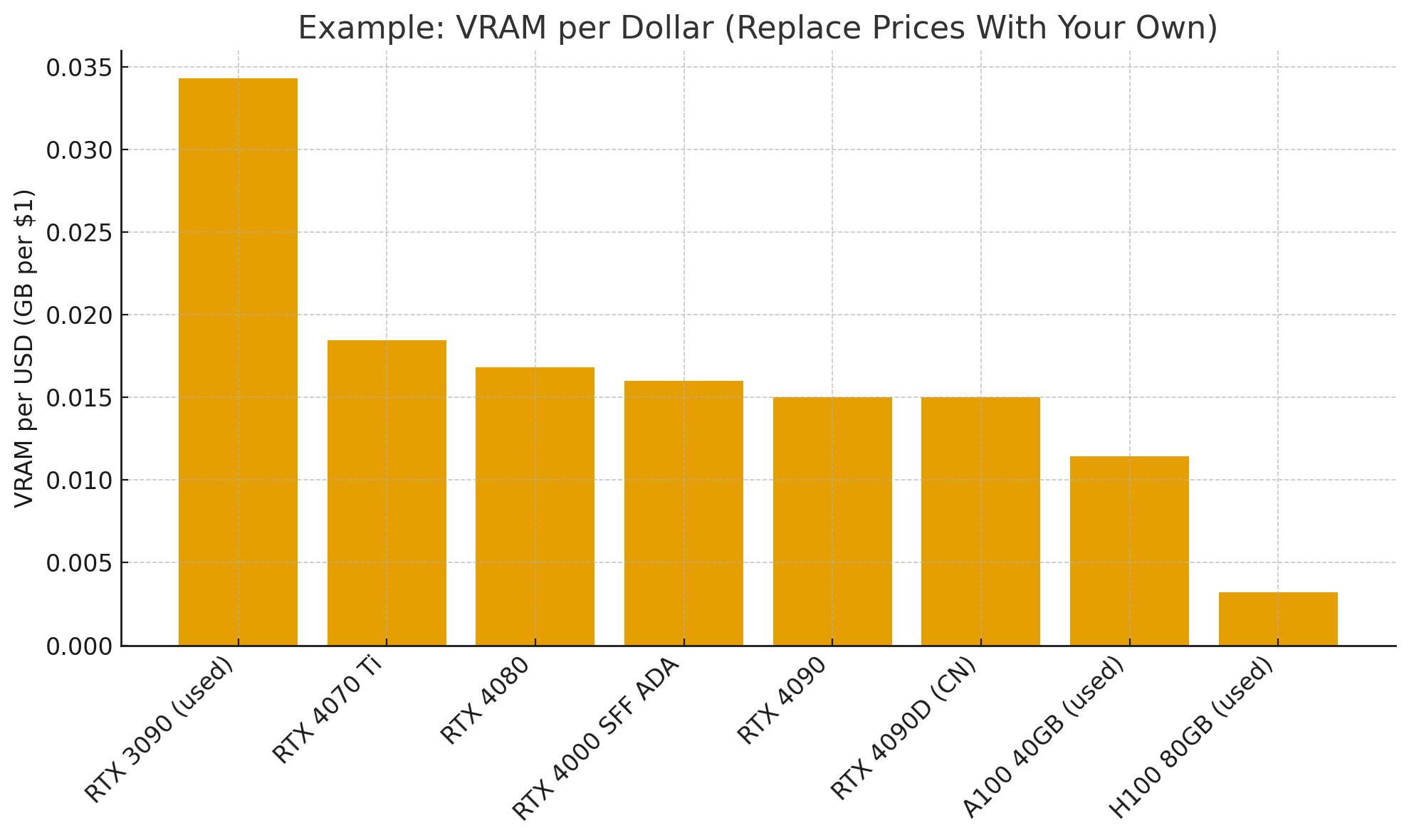
When evaluating GPUs for LLM work, traditional gaming benchmarks become irrelevant. Instead, focus on VRAM per dollar—a metric that reveals surprising value propositions. A used RTX 3090 with 24GB of VRAM at $700-900 offers better value than a new RTX 4070 Ti with 12GB at similar prices, despite the older architecture. For LLM work, VRAM capacity trumps architectural improvements in most cases.
Professional Cards vs Consumer Cards
Professional cards (A100/H100) offer undeniable advantages: massive VRAM pools (40–80GB), NVLink for true multi-GPU scaling, ECC memory for production reliability, and data center-grade cooling solutions. These features matter for production inference servers handling thousands of requests or research institutions training custom models.
However, the downsides are equally significant. Prices start at $10,000+, power requirements often exceed standard PSUs, cooling solutions require a server chassis, and the complexity is too great for typical local deployments. Unless you are building production infrastructure or have specific enterprise requirements, these cards represent significant overkill.
Consumer RTX cards are the pragmatic choice for 99% of local LLM users. They fit standard desktop cases, work with regular power supplies, run quietly enough for office environments, and cost a fraction of professional cards.
Matching LLMs to Your GPU: What Can You Run?
Here are some of the best models you can run, categorized by the VRAM on your GPU.
Best LLMs for 8GB VRAM (2026)
| GPU VRAM | Model | Quantization | Why / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8GB | Mistral 7B | INT4 | Great balance of speed and quality for general use. |
| 8GB | Llama 3.2 7B | INT4 | Smooth on consumer GPUs; strong multilingual support. |
| 8GB | Phi-4 Mini | INT4 | Compact model from Microsoft; excellent for coding tasks than Phi-3. |
| 8GB | Gemma 7B | INT4 | Efficient Google model optimized for modest hardware. |
Best LLMs for 12GB VRAM (2026)
| GPU VRAM | Model | Quantization | Why / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12GB | Llama 3.1 13B | INT4 | Top choice for conversation and reasoning on mid-range GPUs. |
| 12GB | CodeLlama 13B | INT4 | Specialized for programming; solid code completion and Q&A. |
| 12GB | Mistral-Nemo 12B | INT4 / INT8 | Fits comfortably with room for context; good generalist. |
| 12GB | Yi-1.5 9B | INT8 | Strong long-context performance with stable 8-bit runs. |
Best LLMs for RTX 4090 (24GB VRAM)
| GPU VRAM | Model | Quantization | Why / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24GB (RTX 4090) | Llama 3.1 70B | INT4 | Flagship local performance for complex reasoning and depth. |
| 24GB (RTX 4090) | Mixtral 8x7B | INT4 (MoE) | Mixture-of-Experts with GPT-4-class results on many tasks. |
| 24GB (RTX 4090) | DeepSeek Coder 33B | INT4 | Superior for software development, debugging, and code synthesis. |
| 24GB (RTX 4090) | Qwen 2.5 32B | INT4 | Excellent multilingual and mathematical capabilities. |
For models under 7B parameters (Small Language Models), see our SLM and LLM comparison guide for tailored deployment recommendations.
Exploring Video Models: Once you have your local LLM running, you can use it to brainstorm creative ideas for other media. With the rapid rise of US and Chinese AI video generators, many users are now pairing their local models with video AIs. Check out our guide on how to access Veo 3 free to get started. You can even use your local LLM to draft detailed prompts for high-quality video generation.
Unsure what your current GPU can handle? Match models to your hardware in seconds with Nut Studio's compatibility check.
NVIDIA GPU Alternatives: More Options and Apple Silicon
While NVIDIA offers the smoothest experience, other options exist for those willing to experiment or who have different priorities.
1 AMD GPUs: High VRAM, More Tinkering
AMD's flagship RX 7900 XTX offers strong hardware specifications—24GB of VRAM and ~960 GB/s bandwidth—often matching the RTX 3090/4090 at a lower price. However, its main drawback lies in software support. While ROCm, AMD's compute platform and CUDA alternative, has improved significantly, it still lags behind in framework compatibility and ease of use. It often requires manual configuration and lacks out-of-the-box support for many tools.
For users comfortable with Linux and troubleshooting, it can be a viable option, but Windows users are generally better served by NVIDIA.
2 Apple Silicon: A Unified Memory Powerhouse
Apple Silicon (M1 ~ M4 series) introduces a unique unified memory architecture where system RAM and VRAM are shared. Current Mac Studio models with an M3 Ultra support up to 512GB of unified memory and over 800GB/s bandwidth, enabling very large language models to run entirely in memory. On price, a base M3 Ultra Mac Studio ($3,999) with 96GB of unified memory costs less than a single high-end professional GPU.
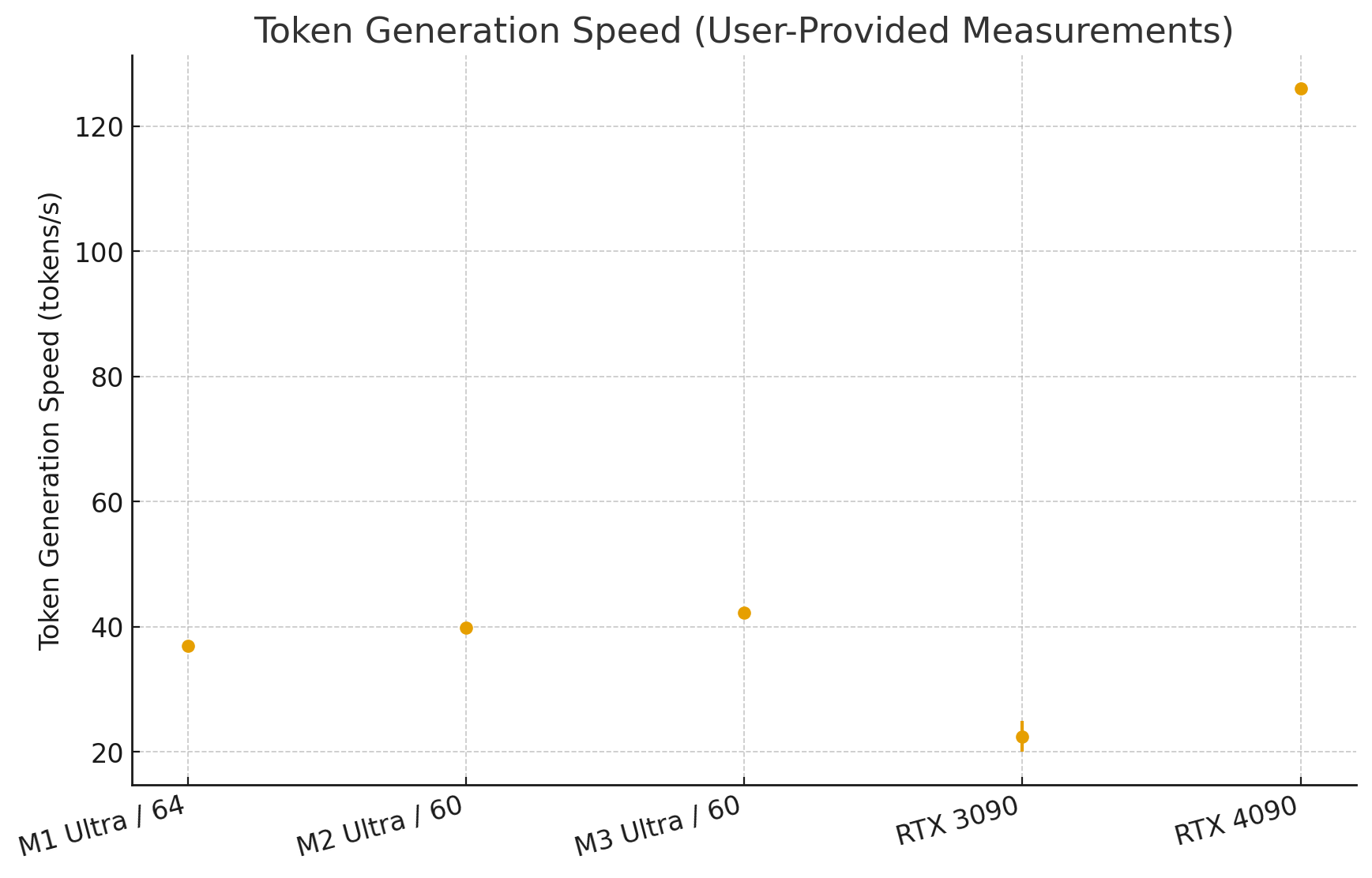
However, token generation speeds lag behind dedicated GPUs—expect 5-15 tokens per second versus 30-50 on an RTX 4090. Apple Silicon excels for experimentation with large models and development work where response speed isn't critical. For production deployments requiring fast inference, dedicated GPUs remain superior.
3 The Experimental Zone: Intel and Regional Players
Intel Arc GPUs represent an interesting wildcard. The A770 (16GB VRAM) offers substantial memory at competitive prices, but software support remains embryonic. Intel's commitment to AI acceleration is clear, but the ecosystem needs time to mature. Consider Intel Arc only for experimentation, not production use.
Regional alternatives like Huawei GPUs face availability challenges outside their home markets. While technically capable and attracting a high level of attention and discussion, obtaining hardware and accessing documentation presents significant barriers for most users.

- Automatically detects your GPU and recommends compatible models
- One-click deployment without manual configuration
- Optimizes model selection based on your hardware capabilities
- Supports all major GPU brands including NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1 What's the Minimum GPU for Running Local LLMs?
The absolute minimum for meaningful LLM work is a GPU with 8GB of VRAM. This allows you to run 7B parameter models with 4-bit quantization, providing ChatGPT-3.5-like capabilities. However, 12GB of VRAM (RTX 3060 12GB, RTX 4070) offers much better flexibility, allowing you to run 7B models at higher precision or experiment with 13B models. Below 8GB, you're limited to very small models. We also have a guide for SLM and LLM comparison.
2 Can I Run 70B Models on A Single Consumer GPU?
Running 70B models on a single consumer GPU requires aggressive optimization. The RTX 4090 or RTX 3090 (both with 24GB VRAM) can technically run 70B models using 4-bit quantization, which reduces the memory requirement to approximately 35GB. However, this requires techniques like offloading some layers to system RAM, which significantly impacts performance. For better 70B model deployment, consider dual-GPU setups or cloud solutions.
3 Is NVIDIA better than AMD for local AI models?
For most people, NVIDIA is the safer and smoother choice because of its mature CUDA ecosystem and near-universal framework support. AMD can be a great value (more VRAM per dollar) if you're on Linux, your card is on the ROCm support list, and you don't mind some tinkering.
If you want the least friction and widest software compatibility, choose NVIDIA. If you're Linux-savvy and chasing maximum VRAM per dollar while accepting some tinkering, AMD can be worthwhile.
4 Can Intel GPUs Run Local Language Models?
Intel Arc GPUs can technically run language models through frameworks like llama.cpp and IPEX-LLM, but support remains experimental. The Arc A770 with 16GB VRAM has sufficient memory for many models, but performance optimization lags behind NVIDIA and AMD. Driver updates are frequent but sometimes unstable, and community support is limited. Intel Arc represents an interesting future option as the ecosystem matures, but it's not recommended for users who need reliable LLM deployment today.
Conclusion
The NVIDIA RTX 5090 is the definitive choice for users demanding the absolute best performance and future-proofing. The RTX 4090 remains a powerful, current-generation option for high-end inference. The used RTX 3090 offers the best value, providing the crucial 24GB of VRAM for a significantly lower price point.
No matter which hardware you choose, remember that Nut Studio can simplify the process: for users starting their local LLM journey who want to avoid the complexity of manual setup, Nut Studio offers automated deployment progress that detects hardware capabilities and optimizes model selection accordingly.
-
Best Animes to Learn Japanese in 2025
Discover 14 anime perfect for learning Japanese, from beginner to advanced levels. Get practical tips on using anime and AI to improve your Japanese skills effectively.
10 mins read -
How ChatGPT Helps with Tests: 10 Methods for Preparation
Learn 10 best ways to use ChatGPT for test and exam prep. Get personalized quizzes, instant feedback, and study smarter for SAT, TOEFL, university finals & more.
6 mins read -
How to Use ChatGPT to Learn a Language? 5 Free Ways Tested
Unlock fluency faster with AI language learning. Get 5 powerful ChatGPT strategies and prompts for personalized vocabulary, grammar, and speaking practice.
10 mins read -
20 Things You Should Never Tell ChatGPT
Stop letting ChatGPT waste your time. Discover 20 things that AI kill your focus and efficiency, while also learning the essential security rules to work safely.
10 mins read -
Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing in 2025 [Templates Included]
Discover best ChatGPT prompts for academic writing. Get templates for each step that actually work. Test locally with Nut Studio.
10 mins read -
Best LLMs for Resume Writing: Cloud vs. Local[2025 Tested]
Unbiased 2025 review of the best LLMs for resume writing—Claude 4, Gemini 2.5 Pro, GPT-5, Llama 3.2, Mistral, Phi-4—plus prompts, advanced LLM tips, and local setup.
5 mins read
 Nut Studio
Nut Studio












Was this page helpful?
Thanks for your rating
Rated successfully!
You have already rated this article, please do not repeat scoring!