
Finding the best LLM for translation in 2025 isn't easy. There are so many models out there, each claiming to be better than the rest. As someone who's tested dozens of them—both online and offline—I know how confusing it can be if you're just starting out.
That's why I wrote this guide. I'll walk you through everything I've learned from hands-on testing: which LLM translation models really work, how they're evaluated, and which ones you can trust for different tasks—like translating websites, documents, or even casual chat. Let's get started!
CONTENT:
- LLM Translator Benchmark: How Are Translation Models Evaluated?
- [2025 Update] 10 Best LLMs for Translation (With Real Benchmark Data)
- 1. DeepSeek‑V3
- 2. Gemini 3.0
- 3. GPT‑5.1
- 4. Claude 4 Opus / 3.5 Sonnet
- 5. Qwen 3 (72B) / 2.5
- 6. DeepL (Translator)
- 7. Mistral Large 2 (123B)
- 8. Llama 4 Scout / 3.3 (70B)
- 9. Yi‑Lightning / Yi‑1.5
- 10. LLaMA 3.1 8B Instruct
- LLMs vs Traditional Machine Translation (NMT): What's the Real Difference?
- How to Run LLM Translation Locally (Offline)?
- FAQs About LLMs for Translation
- Conclusion
LLM Translator Benchmark: How Are Translation Models Evaluated?
When I started testing LLM translation models, I quickly realized not all of them are built the same. Some sound fluent but miss key details. Others get the facts right but feel robotic. So how do we actually judge which translate models are good?
Researchers—and now even everyday users like me—use a few key metrics called LLM accuracy metrics to evaluate translations. Here's how it works, in plain English:
| Aspect | LLM Translation | Traditional NMT | Notes / Impact for You |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluency & Naturalness | Produces more fluent, natural text | Often literal, less smooth | Best LLMs offer better reading experience |
| Context Handling | Understands document-level context | Translates sentence-by-sentence | LLMs keep ideas connected better |
| Accuracy in Specialized Fields | Struggles with medical, legal terms; prone to hallucinations | Usually more precise in specialized terminology | Use caution with LLMs in critical areas |
| Adaptability | Learns style or tone from few examples | Fixed models, less flexible | LLMs can match your desired voice or style |
| Deployment Options | Can run locally, offline with tools like Nut Studio | Usually cloud-based, requires internet | Local deployment means privacy, no delays |
| Resource Requirements | Requires strong hardware for large models | Generally lighter, cloud offloads processing | Small LLMs run well on personal PCs; ideal with Nut Studio |
| Language Coverage | Covers many languages, but quality varies | Mature for high-resource languages | LLMs improving fast, NMT still strong for niche languages |
As you can see, no single metric is perfect. That's why in this article, I rely on a mix of tests, real-world tasks, and human judgment. I don't just look at scores—I actually run these models myself.
Coming up next, I'll show you which models came out on top in 2025 when tested across these areas.
[2025 Update] 10 Best LLMs for Translation (With Real Benchmark Data)
If you're wondering which AI model handles translation best, we tested and ranked 10 top small LLMs for translation. These aren't giant 100B+ parameter behemoths — we focused on models that are actually deployable offline on regular hardware. Why? Because:
- Large models like GPT-5.1 and Claude Opus often require API or cloud access, making them hard to run privately.
- Smaller models are now good enough for day-to-day translation tasks, especially in English ↔ Chinese, French, Spanish, etc.
- With LLM deployment tools , you can run these models fully offline with just one click — no coding, no setup.
We evaluated each model using real translation benchmarks (like BLEU, COMET, FLORES200), and also judged how well they handle context, terminology consistency, and local deployment. Here's the full comparison table:
| Model | Rating (Translation) | Translation Quality | Semantic Understanding | Domain Adaptation | Reasoning (Culture/Metaphor) | Best Use Case / Focus | Local Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek‑V3 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Exceptional | Excellent | Tech, code, complex | Strong | Technical & code‑heavy | ⚠️ Heavy (24–48GB; full MoE API) |
| Gemini 3.0 Pro (Google) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Excellent | Excellent | Long, multimodal docs | Strong | Ultra‑long, multimodal | ❌ API‑only |
| GPT‑5.1 (OpenAI) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Excellent | Excellent | Legal, tech, creative | Excellent | All‑round, high‑end | ❌ API‑only |
| Claude 4 Opus / 3.5 Sonnet | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Very strong | Excellent prose | Legal, literary | Excellent | Tone‑sensitive text | ❌ API‑only |
| Qwen 3 (72B) / 2.5 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Strong | Strong | Asian langs, tech | Good | CN/JP/KR focus | ⚠️ Heavy (24–48GB) |
| DeepL (Translator) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐½ | Strong | Good | Biz / legal docs | Moderate | High‑volume text | ❌ Cloud / enterprise |
| Mistral Large 2 (123B) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Solid | Very strong | EU langs (FR/DE/ES) | Good | Enterprise throughput | ⚠️ Heavy (128GB+) |
| Llama 4 Scout / 3.3 (70B) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Solid | Strong logic | Docs, long context | Good | Document analysis | ⚠️ Heavy (48GB+) |
| Yi‑Lightning / Yi‑1.5 | ⭐⭐⭐½ | Good | Stable | Fast | Moderate | Cost‑efficient | ✅ 16–24GB; API |
| LLaMA 3.1 8B Instruct | ⭐⭐⭐½ | Decent | Decent | General, small edge | Basic | Local / mobile‑edge | ✅ 8–12GB |
1 DeepSeek‑V3 — Top Open‑Weight for Technical & Code‑Heavy Translation
If you want one of the strongest open‑weight models you can still self‑host, DeepSeek‑V3 is a top pick. It excels at technical, code‑adjacent, and complex documents while keeping translations precise and natural.
Here's what stood out:
- Exceptional technical accuracy: Great for API docs, specs, and engineering content.
- Clean, idiomatic output: Feels “native” in English and Chinese, even with jargon.
- Strong reasoning: Handles step‑by‑step explanations and code comments without losing context.
Best use cases:
- Technical manuals, product docs, and developer portals.
- Code comments, commit messages, and dev‑facing UI copy.
- Teams who need a strong self‑hosted alternative to closed APIs.
DeepSeek‑V3’s distilled 70B‑class checkpoint is heavy (24–48GB VRAM for smooth use). The full MoE version is API‑only. For smaller GPUs, use a quantized build via tools like Nut Studio to keep it practical on consumer hardware.
2 Gemini 3.0 Pro — Multimodal & Long‑Form Translation Workhorse
Gemini 3.0 Pro is built for very long and multimodal documents. If you're translating PDFs with charts, images, and mixed layouts, its long context and document reasoning make it stand out.
Here's what stood out:
- Ultra‑long context: Handles book‑length or report‑level translations with fewer consistency breaks.
- Multimodal support: Can read and reason over images, tables, and diagrams inside documents.
- Smooth discourse: Keeps terms and style consistent across sections and pages.
Best use cases:
- Whitepapers, annual reports, and technical PDFs with visuals.
- Enterprise translation pipelines on Google Cloud.
- Apps that mix translation with document understanding and UI generation.
Gemini 3.0 Pro is closed‑source and API‑only (Vertex AI, Google AI Studio). It’s ideal for teams already on Google Cloud, not for fully offline or on‑device setups.
3 GPT‑5.1 — Universal High‑End Translator & Agent Core
GPT‑5.1 is a top‑tier general translator across most major language pairs. It’s especially strong when you also need reasoning, coding, or agent workflows in the same system as your translations.
Here's what stood out:
- Consistently strong across pairs: Great for EN↔EU, EN↔Asian, and many low‑resource directions.
- Balanced style control: Easily switches between formal, neutral, and casual tone.
- Agent‑friendly: Fits well into workflows that mix translation with coding, extraction, or summarization.
Best use cases:
- End‑to‑end localization pipelines (translate → review → adapt).
- AI agents that read, translate, and act on documents or websites.
- High‑stakes translation where nuance and reasoning both matter.
GPT‑5.1 is API‑only through OpenAI. It delivers some of the best quality available, but you can’t run it locally or fully offline.
4 Claude 4 Opus / 3.5 Sonnet — Best for Tone & Literary‑Style Translation
If you care about beautiful prose, tone, and style, Claude 4 Opus and Claude 3.5 Sonnet are excellent choices. They’re particularly strong for French, German, and other European languages where wording really matters.
Here's what stood out:
- Superior prose quality: Translations read like professionally edited text.
- Tone‑aware: Preserves humor, politeness, and formality between languages.
- Stable on long docs: Keeps arguments and narrative threads consistent over thousands of words.
Best use cases:
- Literary content, marketing copy, and high‑end editorial work.
- Legal memos, policy docs, and academic essays where register is critical.
- Teams needing API‑based translation with strong privacy controls.
Claude models are closed‑source and cloud‑hosted by Anthropic. They’re great for API workflows, but not for fully offline translation.
5 Qwen 3 (72B) / 2.5 — Open‑Weight Powerhouse for Asian Languages
Qwen 3 / Qwen 2.5 continues Alibaba’s strong focus on Chinese and Asian language pairs. If you want a self‑hosted model that excels at CN/JP/KR and technical content, this is a top multilingual open‑weight pick.
Here's what stood out:
- Excellent for CN/JP/KR: Strong handling of idioms, formal writing, and tech jargon.
- Stable terminology: Keeps product names and legal terms consistent across long texts.
- Open‑weight control: Can be fine‑tuned or constrained for internal workflows and policies.
Best use cases:
- Chinese, Japanese, and Korean localization for apps and products.
- On‑prem translation for companies with strict data requirements.
- Technical docs, manuals, and support content in Asian markets.
Qwen 3 (72B) is large — expect 48GB+ VRAM for the full model. Smaller 7B–32B or quantized builds are better for 24GB cards and easy local deployment with tools like Nut Studio.
6 DeepL — Specialized NMT for High‑Volume Documents
DeepL isn’t a general LLM, but it’s still one of the strongest pure translation engines for many European language pairs. It shines when you care about speed, formatting, and reliability at scale more than creative reasoning.
Here's what stood out:
- Production‑grade stability: Very few glaring errors across business and legal docs.
- Good formatting: Preserves paragraphs, bullet lists, and basic layout.
- Fast and scalable: Optimized for batch and API workloads, not experimentation.
Best use cases:
- Bulk translation of contracts, manuals, and internal documents.
- Enterprises that need predictable output across many files.
- Workflows where specialized NMT is enough and LLM reasoning isn’t required.
DeepL is a cloud / enterprise service. You don’t get full LLM flexibility, but you do get strong, fast, and consistent translation for supported language pairs.
7 Mistral Large 2 (123B) — Strong Enterprise Model for European Languages
Mistral Large 2 targets enterprise‑scale workloads, with a focus on European languages. It offers very strong multilingual consistency and high throughput for FR/DE/ES and related pairs.
Here's what stood out:
- Reliable EU‑language coverage: Especially good for French, German, and Spanish.
- Consistent terminology: Stable wording across long documents.
- Enterprise‑oriented: Tuned for performance and robustness in production pipelines.
Best use cases:
- High‑throughput EU localization for SaaS and web products.
- Internal tools for FR/DE/ES document translation.
- Companies that want a large model with strong European language focus.
The full 123B model is very heavy and typically runs on large GPU nodes (128GB+ VRAM). For smaller setups, consider Mistral’s medium‑sized or Mixture‑of‑Experts models instead.
8 Llama 4 Scout / LLaMA 3.3 (70B) — Long‑Context Open‑Weight for Documents
Llama 4 Scout / LLaMA 3.3 70B is designed for long‑context document work. If you need an open‑weight model that can read, analyze, and translate long files in one go, this line is worth a look.
Here's what stood out:
- Very long context: Handles multi‑chapter or large report translation in a single session.
- Strong logic: Good at preserving document structure and argument flow.
- Open‑weight flexibility: Easier to integrate into custom, self‑hosted document pipelines.
Best use cases:
- Document analysis + translation (e.g., summarize then translate).
- Knowledge base localization for wikis and help centers.
- Teams that need long‑context open‑source models on‑prem.
The 70B class is still heavy — expect 48GB+ VRAM or strong quantization. For simpler tasks, lighter LLaMA variants (8B–13B) are easier to run with Nut Studio and similar tools.
9 Yi‑Lightning / Yi‑1.5 — Fast, Cost‑Efficient CN↔EN Translation
Yi‑Lightning / Yi‑1.5 aims for high‑speed, cost‑efficient Chinese‑English translation. It’s lighter than many big models while still offering good, stable translations, which makes it ideal for everyday use and smaller deployments.
Here's what stood out:
- Fast inference: Great for real‑time or interactive translation tools.
- Good CN↔EN quality: Keeps everyday tone and meaning intact.
- Resource‑friendly: Runs well on 16–24GB, especially when quantized.
Best use cases:
- Chatbots and customer service tools for CN↔EN users.
- Educational and learning apps for bilingual users.
- Small teams that want a fast, low‑cost CN↔EN engine.
Yi‑Lightning models are designed to be efficient. They run on 16–24GB GPUs and can also be accessed via API, making them a nice middle ground between tiny local models and heavy cloud giants.
10 LLaMA 3.1 8B Instruct — Small but Capable Local Translator
LLaMA 3.1 8B Instruct is one of the smallest models that still gives decent translation quality. If you care about running everything locally on modest hardware (or even mobile‑edge), this is a very good starting point.
Here's what stood out:
- Surprisingly capable for 8B: Handles everyday EN↔EU and EN↔CN translations reasonably well.
- Low resource use: Runs on 8–12GB VRAM, especially with 4‑bit quantization.
- Good generalist: Also works for summarization, Q&A, and light coding besides translation.
Best use cases:
- Offline translation on laptops or small desktops.
- Mobile‑edge or embedded deployments where size is critical.
- Hobby projects and personal productivity tools that must stay local.
Want to try LLaMA‑class models locally without touching a terminal? Tools like Nut Studio let you deploy LLaMA 3.x in a few clicks on Windows.
LLMs vs Traditional Machine Translation (NMT): What's the Real Difference?
When choosing between llm translation and traditional neural machine translation (NMT), it helps to understand their key differences. To make it clearer, here's a quick comparison table that breaks down their strengths and weaknesses.
| Evaluation Area | Metric(s) | What It Checks | Limitation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Translation Quality | BLEU, COMET, FLORES-200 | Word/meaning overlap with human reference translations. COMET uses neural scoring. | BLEU ignores synonyms and tone. COMET is slower. | Comparing best llm for translations in common language pairs. |
| Semantic Understanding | METEOR, COMET | Tests how well the model handles synonyms, paraphrasing, and sentence logic. | Still misses deeper context and sarcasm. | Long paragraphs or complex topics like essays. |
| Terminology Consistency | Manual review / COMET | Checks if key terms stay the same across multiple sentences. | Hard to automate fully, COMET is approximation only. | LLM translator for technical docs or multi-turn chats. |
| Domain Adaptation | BLEU, Human Review | Judges model performance in legal, medical, or financial contexts. | BLEU can’t measure technical accuracy. | Specialized translation llm for industry use. |
| Reasoning Ability | COMET, Human Eval | Looks at understanding of metaphors, idioms, cultural tone. | Hard for automated scores to capture nuance. | Creative writing or casual tone translations. |
| Deployment & Efficiency | FLORES-200, Hardware Benchmarks | Tests if model runs fast, works locally, and fits into memory. | FLORES-200 lacks runtime details. | Choosing a small llm for translation on local devices. |
《Comparing Large Language Models and Traditional Machine Translation Tools for Translating Medical Consultation Summaries – A Pilot Study》
As you can see, using LLMs for translation offers many advantages in fluency and adaptability, especially if you deploy models locally. This means better privacy, faster response times, and more control over your translations. But keep in mind, traditional NMT systems remain strong for specialized, critical tasks.

How to Run LLM Translation Locally (Offline)?
Now that you know the key differences between LLMs and traditional machine translation, the next question is: how do you run an LLM for translation locally?
Running a local LLM for translation means you don't have to send your texts to the cloud. This keeps your data safe and lets you translate faster. From my experience, having a model right on your PC or laptop feels like having a personal translator who's always ready — even without Wi-Fi.
That's where Nut Studio shines. It's a one-stop app that lets you download and run powerful LLMs locally with just a few clicks. No coding or complicated setup needed.

- Privacy first: All your documents stay on your device — no cloud uploading.
- Easy deployment: Supports over 50 popular open-source and proprietary models, including top translation LLMs.
- Fast and offline: Instant responses without internet lag.
- User-friendly interface: Great for beginners and pros alike.
- Knowledge base support: You can upload your own files (like PDFs, PPTs, and TXT) to create a custom reference for the AI.
How to Get Started with Nut Studio for Translation
Step 1: Download and install Nut Studio from the official website.
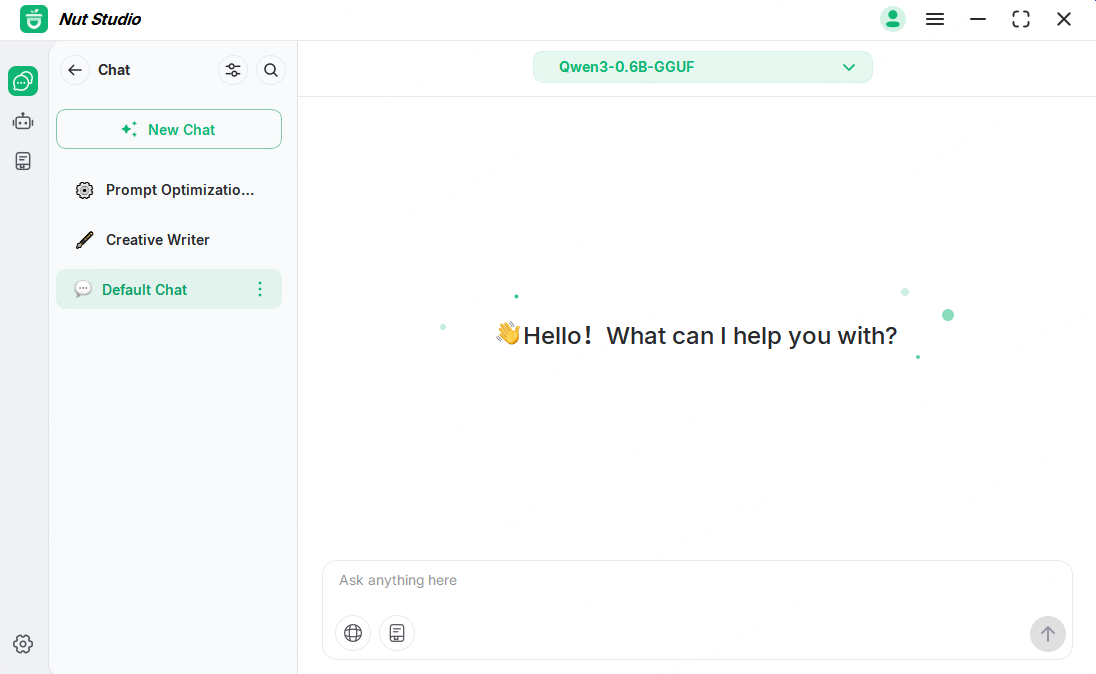
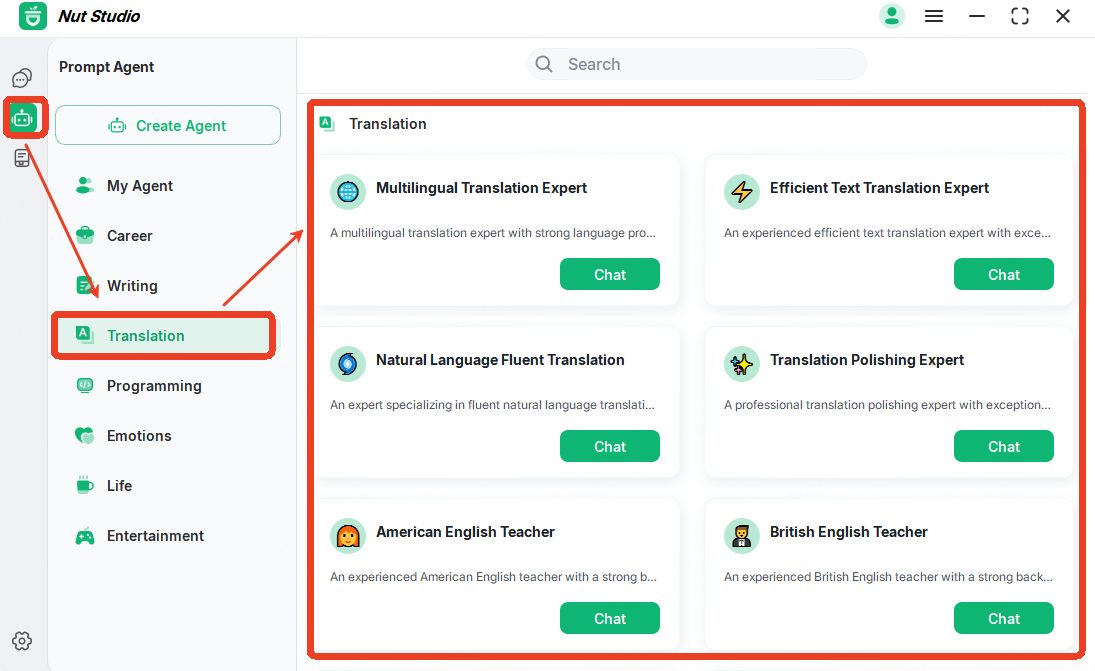
Step 2: Choose a proper translation prompt according to your need.
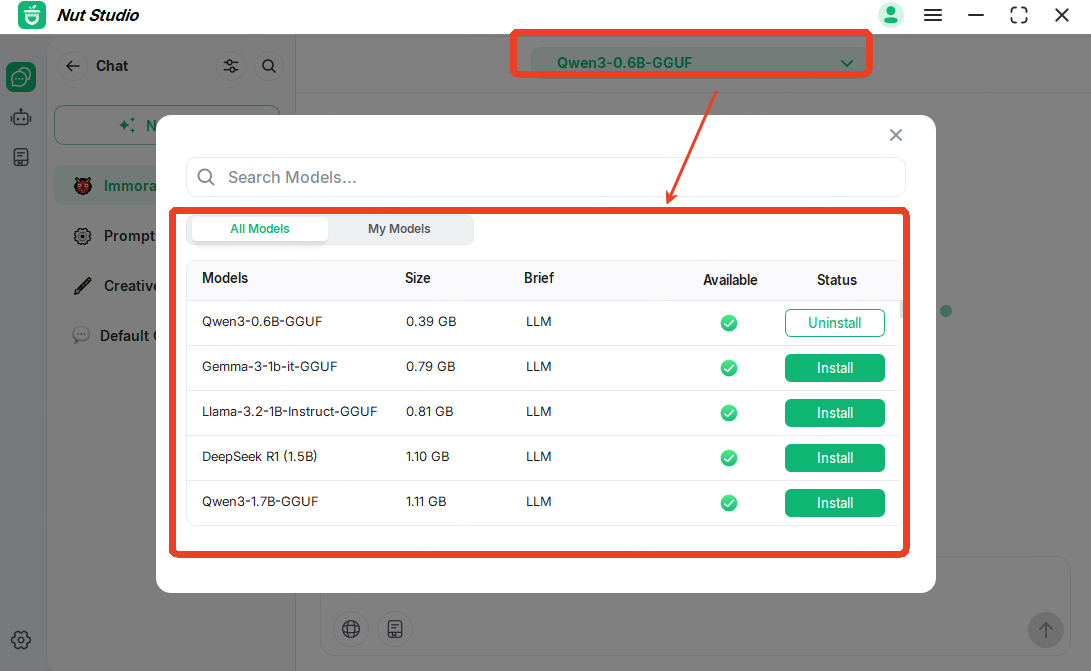
Step 3: Choose a translation model like Qwen1.5 or DeepSeek from the model list.
FAQs About LLMs for Translation
1 Which LLM is best for translation in 2025?
It depends on your needs. GPT‑5.1, Claude 4 Opus / 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 3.0 Pro lead for overall quality via API, while DeepSeek‑V3 and Qwen 3 (72B) / 2.5 are top open‑weight choices you can self‑host. For smaller setups, LLaMA 3.1 8B or Yi‑Lightning / Yi‑1.5 are solid picks. Check our benchmark section for full details.
2 Is NMT better than LLM for translation?
It depends on the task. LLMs offer better context and nuance, especially for complex or creative content. NMT tools like DeepL are usually faster and cheaper for high‑volume, repetitive documents. If you want more control and customizability, LLMs are often the better choice.
3 Can I use LLMs offline for private documents?
Yes. Many top translation models can run fully offline with tools like Nut Studio, which supports local deployment and document upload. It works with formats like PDF, PPT, and TXT — ideal for translating private files securely on your own machine.
4 What are the best small models for edge deployment?
Models like LLaMA 3.1 8B Instruct, Mistral 7B‑class models, and Yi‑Lightning / Yi‑1.5 offer a good balance of size and translation quality. They can run on consumer‑grade GPUs or laptops (8–24GB VRAM), especially using optimized runtimes like GGUF via Nut Studio.
5 Is LLM good for translation?
Yes, if you pick the right ones. Frontier models like GPT‑5.1, Claude 4, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and open‑weights like DeepSeek‑V3 and Qwen 3 / 2.5 reach near‑human quality on many language pairs. For secure, scalable use, local platforms like Nut Studio let you deploy open‑weight models without sending data to the cloud.
Conclusion
In 2025, finding the best LLM for translation means balancing accuracy, fluency, and deployment flexibility. Whether you need domain-specific precision, offline privacy, or lightweight models for local use, this guide shows there's no one-size-fits-all—just the right tool for your workflow. With so many strong open-source and closed-source options now available, it's never been easier to choose the best LLM for translation that fits your exact needs.
 Nut Studio
Nut Studio












Was this page helpful?
Thanks for your rating
Rated successfully!
You have already rated this article, please do not repeat scoring!